Number patterns, including arithmetic and geometric sequences and series
Lesson Category: Grade 12 Lessons
Functions: Formal Definition, Inverse, L1
Functions: Formal Definition , Inverse, exponential and logarithmic
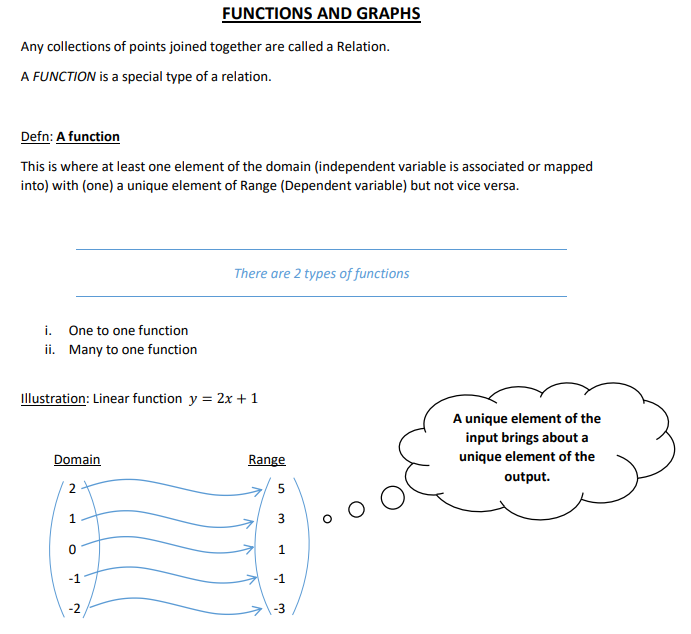
- Definition of a function.
2. General concept of the inverse of a
function and how the domain of the
function may need to be restricted (in
order to obtain a one-to-one function)
to ensure that the inverse is a function.
3. Determine and sketch graphs of the
inverses of the functions defined by
𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑞;
Focus on the following characteristics: domain and range intercepts with the axes,
turning points, minima, maxima, asymptotes (horizontal and vertical), shape and
symmetry, average gradient (average rate of change), intervals on which the function increases /decreases.
Functions: Formal Definition, Inverse, exponential and logarithmic Lesson3
5. Revision of the exponential function and the exponential laws and graph of the function defined by y = b x where b > 0 and b ≠ 0 6. Understand the definition of a logarithm: y = logb x ⇔ x = b y where b > 0 and b ≠ 1 7. The graph of the function, 𝑦 = 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑏 𝑥 for both the cases 0 < 𝑏 < 1 and 𝑏 > 1.
End Of Term1 Grade12 Math.
You are Doing Well. Go ahead and click the Next Topic button.
We are Now Moving to Euclidean Geometry. Good Luck.